Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a buzzword—it’s actually revolutionizing the way we work, live, and interact with the digital world. Among the most exciting under AI is AI agents. Autonomous systems that are revolutionizing industries, enhancing user experiences, and making smarter real-time decisions.
In this all-encompassing guide, we’re going to break down what AI agents are, how they work, where they’re used, and why you need them for the future of technology. Whether you’re a technology aficionado, a digital marketing guru, or a business leader, understanding AI agents will give you an impenetrable foundation to tap into their potential.
1. What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a computer program or a system that possesses the capability to perceive its environment, process the information, and act intelligently to generate desired outcomes—sometimes without human intervention. AI agents leverage a combination of machine learning, natural language processing, neural networks, and data analytics to learn and make decisions based on new information.That is, think of an AI agent as a smart assistant capable of thinking, learning, and doing things—without needing to be told step by step every time.________________________________________
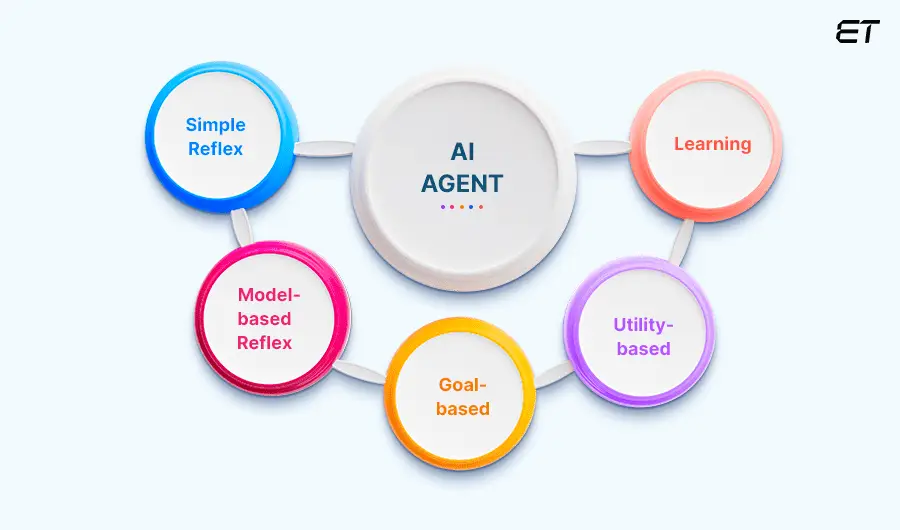
2. Types of AI Agents
AI agents vary based on their capabilities and complexity. Below are the main types:a. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents act only on current perceptions. They don’t remember past experiences. A basic thermostat is a good example.b. Model-Based Agents
These maintain an internal model of the world and make decisions based on both current input and past experiences.c. Goal-Based Agents
These agents make decisions by considering a specific objective and choosing actions that help reach that goal.
d. Utility-Based Agents
They weigh different outcomes based on a utility function—choosing actions that maximize benefit.
e. Learning Agents
These are the most advanced. They learn from past actions and improve over time, making them ideal for dynamic and complex environments.
________________________________________
3. How Do AI Agents Work?
Essentially, AI agents are practicing a sense-think-act loop:
• Sense: The agent takes information from the environment (text, audio, pictures, etc.).
• Think: It processes the input and makes decisions using algorithms and learned data.
• Act: The agent performs on its decisions (e.g., answering a query, moving something, starting a process).
This loop executes continuously, allowing AI agents to react in real time and match newer updates.________________________________________
4. Real-Life Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are incorporated in the majority of aspects of modern life. Some of the most significant sectors that employ them are as follows:
a. Customer Service
Virtual assistants and chatbots like ChatGPT or Google Assistant are AI agents designed to handle customer queries, reducing response times and taking the load off humans.
b. Healthcare
AI agents are applied in diagnosing diseases, analyzing scans, personalizing treatment plans, and even remotely tracking patients.
c. Finance
AI agents assist in detecting fraud, automating trading, and making financial recommendations based on the behavior of consumers.
d. E-commerce
From product suggestions to route planning, AI agents facilitate online purchasing and personalize it.
e. Smart Homes
Voice-controlled devices like Alexa or Siri utilize AI agents to manage lights, appliances, and so forth—enabling a seamless life experience.
5. Benefits of AI Agents
Here’s why businesses and individuals are investing in AI agents:
• 24/7 availability – They work without fatigue.
• Speed and efficiency – Decisions are made faster than humans.
• Consistency – No human error or bias.
• Scalability – Can handle thousands of interactions simultaneously.
• Learning capabilities – Improves over time with data exposure.
________________________________________
6. Challenges Facing AI Agents
Despite their potential, AI agents are not without issues:
• Data Privacy: Misuse of user data is a serious concern.
• Bias in Training Data: AI can inherit and amplify human biases.
• Transparency: Decisions made by AI agents can be hard to interpret.
• Dependency: Overreliance on AI could reduce human skill levels.
• Security: They can be targeted by cyber threats.
________________________________________
7. AI Agents vs. Traditional Software
Here’s how AI agents differ from standard software systems:
Feature Traditional Software AI Agents
Adaptability Static Learns & evolves
Decision-making Rule-based Autonomous & data-driven
Context-awareness Low High
Learning ability None Yes
Human Interaction Minimal Natural language interfaces
AI agents are more human-like in how they operate—making them better suited for complex and dynamic tasks.
________________________________________
8. The Future of AI Agents
We are moving towards an era where AI agents will become digital coworkers, virtual doctors, legal assistants, and more. Here are some future trends:
• Multi-agent systems that collaborate to solve bigger problems.
• Emotion-aware agents that can detect and respond to human feelings.
• Fully autonomous agents handling advanced tasks like driving, negotiating deals, or creating content.
• AI Agents in Metaverse—enhancing virtual worlds with intelligent interactions.
________________________________________
9. Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
As AI agents get more and more integrated into society, we must address ethical challenges:
• Who is accountable in case an AI agent makes a negative decision?
• How can we offer fairness and equity in AI decision-making?
• What regulations are needed to ensure safe deployment?
Developers and organizations must create open, fair, and ethical systems that give user safety and data privacy top priority.
________________________________________
10. How to Get Started with AI Agents
Want to develop or use AI agents? Here is a simple guide:
1. Learn the Basics: Get familiar with AI principles of machine learning, NLP, and reinforcement learning.
2. Use Pre-baked Tools: Dialogflow, IBM Watson, and Microsoft Bot Framework offer pre-existing AI agent templates.
3. Experiment: Start small—create a chatbot or personal assistant with Python libraries like Rasa or spaCy.
4. Scale incrementally: As business grows, add APIs, scale capabilities, and scale into automation.
5. Stay Up to Date: AI is evolving at warp speed—research articles, conferences, and developer forums.
________________________________________
Conclusion: Tapping the Power of AI Agents
AI agents are no longer in the realm of science fiction—they are here and in the future today. They boost productivity, automate tasks, and enable unprecedented personalization. As these systems continue to develop, they will transform industries and redefine peoples’ interaction with machines.
But with such abilities comes responsibility. It is essential that these agents be deployed and devised in an ethical way, safely and openly.
Whether you’re a developer looking to create smarter applications, a business aiming to optimize workflows, or just curious about tech trends, AI agents offer limitless opportunities. Now is the time to explore, innovate, and lead in this AI-powered future.opportunities. Now is the time to explore, innovate, and lead in this AI-powered future.
🤖 AI Agents: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What exactly is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a computer program that can perceive its environment, process information, and take intelligent actions to achieve specific goals—often without constant human intervention.
2. How are AI agents different from traditional software?
Unlike traditional rule-based software, AI agents can learn from data, adapt to changes, make decisions autonomously, and interact with users using natural language.
3. What are some real-world examples of AI agents?
- Virtual assistants (like Alexa, Siri, ChatGPT)
- Chatbots for customer service
- Fraud detection systems in finance
- Smart healthcare tools for diagnosis
- Home automation devices like smart thermostats
4. Do AI agents always need human input?
No. While some AI agents require initial training or setup, many can operate independently, adapt over time, and make decisions on their own.
5. Are all AI agents the same?
No. There are several types:
- Simple Reflex Agents
- Model-Based Agents
- Goal-Based Agents
- Utility-Based Agents
- Learning Agents
- Each type has different levels of intelligence and adaptability.
6. How do AI agents make decisions?
AI agents follow a loop:
- Sense (gather input) → Think (analyze using AI models) → Act (respond or execute a task).
- They use data, rules, and learned patterns to choose the best action.
7. What are the benefits of using AI agents?
- Operate 24/7 without fatigue
- Make fast and consistent decisions
- Handle thousands of tasks simultaneously
- Learn and improve over time
- Enhance user experiences
8. Are there risks or challenges with AI agents?
Yes, including:
- Data privacy concerns
- Bias in decision-making
- Security vulnerabilities
- Lack of transparency
- Over-dependence on AI systems
9. What industries use AI agents the most?
- Customer Service
- Healthcare
- Finance
- E-commerce
- Smart Homes
- Education
10. Can I build my own AI agent?
Absolutely! Start by learning Python, machine learning, and natural language processing. Use platforms like Dialogflow, Rasa, or Microsoft Bot Framework to build your own AI assistants or bots.
11. Will AI agents replace human jobs?
AI agents are more likely to augment human work rather than completely replace it. They take over repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more strategic, creative, or empathetic roles.
12. Are AI agents safe to use?
AI agents are generally safe when developed responsibly. However, it’s important to ensure ethical guidelines, strong data security, and transparent decision-making processes.
13. What is the future of AI agents?
In the future, AI agents will:
Collaborate in multi-agent systems
Understand human emotions
Operate in virtual worlds (Metaverse)
Take on roles like digital coworkers, advisors, and creators